Prostate Artery Embolization
Prostate artery embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia, a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate gland. Prostate artery embolization involves the injection of small particles into the arteries that supply blood to the prostate gland, causing it to shrink in size and reduce symptoms related to benign prostatic hyperplasia.
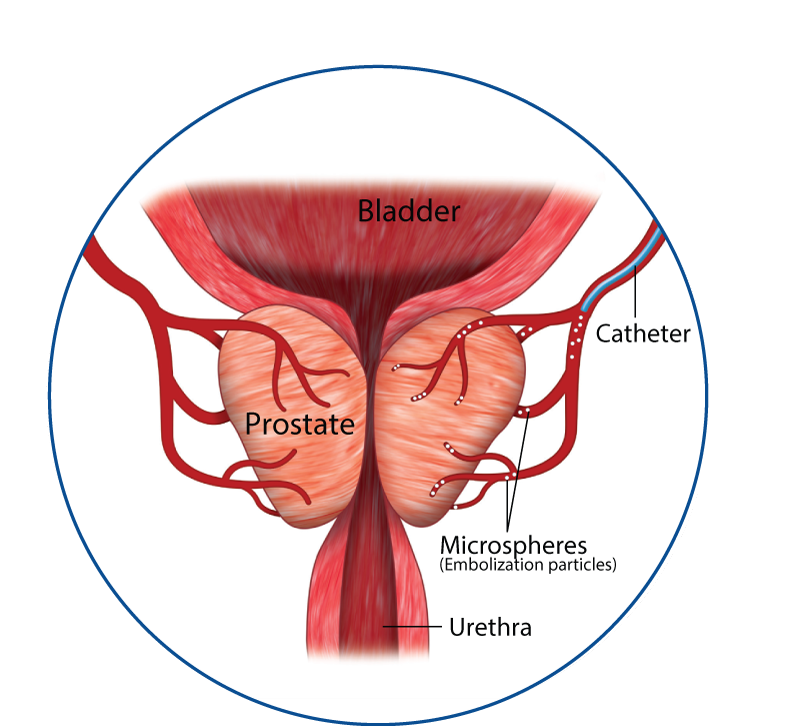
Benign prostatic hyperplasia is a common condition that affects many men as they age. It is caused by the growth of prostate tissue, which can constrict the urethra and interfere with the flow of urine. Common symptoms of benign prostatic hyperplasia include frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urine flow, weak urine flow, and the feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder. These symptoms can significantly impact a man’s quality of life, leading to decreased mobility, increased risk of falls, and social isolation.
Traditionally, the standard treatment for benign prostatic hyperplasia has been transurethral resection of the prostate, a surgical procedure in which excess prostate tissue is removed through the urethra. While transurethral resection of the prostate is effective in relieving symptoms, it is associated with a high risk of complications, including bleeding, infection, and erectile dysfunction. Additionally, transurethral resection of the prostate requires a general anesthetic and several days of hospitalization, leading many men to avoid seeking treatment until their symptoms become severe.
Prostate artery embolization has emerged as an alternative treatment option for benign prostatic hyperplasia in recent years. This procedure involves the injection of small particles, typically made of plastic or gelatin, into the arteries that supply blood to the prostate gland. The particles block the blood vessels, reducing blood flow to the prostate and causing it to shrink in size. Prostate artery embolization is typically performed under local anesthesia, and most patients are able to return home the same day.
One of the key advantages of Prostate artery embolization over traditional surgical treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia is that it is a minimally invasive procedure that can be performed on an outpatient basis, reducing the risk of complications and allowing patients to return to their normal activities more quickly. Additionally, Prostate artery embolization does not require general anesthesia, which can be particularly beneficial for older patients or those with underlying health conditions that make anesthesia risky.
Several studies have demonstrated the safety and effectiveness of Prostate artery embolization for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. One study published in the Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology in 2014 followed 30 men who underwent Prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia. The study found that Prostate artery embolization was effective in reducing BPH symptoms, with an average improvement in International Prostate Symptom Score (IPSS) of 67% at 12 months. The study also found that Prostate artery embolization was associated with few complications, with no cases of major bleeding or urinary incontinence reported.
Another study published in the Journal of Urology in 2016 compared the efficacy of Prostate artery embolization and transurethral resection of the prostate for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia. The study followed 200 men, with half undergoing Prostate artery embolization and half undergoing transurethral resection of the prostate. The study found that both procedures were equally effective in relieving benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms, with similar improvements in IPSS scores and maximum urine flow rates. However, Prostate artery embolization was associated with a lower risk of complications, including bleeding and sexual dysfunction.
Despite the growing body of evidence supporting the use of Prostate artery embolization for the treatment of benign prostatic hyperplasia, there are still some limitations to the procedure. Not all men with benign prostatic hyperplasia are suitable candidates for Prostate artery embolization, particularly those with very large prostates or significant bladder outlet obstruction. Additionally, Prostate artery embolization is a relatively new procedure and may not be widely available in all areas.
Another limitation of Prostate artery embolization is the lack of long-term data on its effectiveness and safety. While studies have shown promising results at one and two-year follow-ups, there is a need for longer-term studies to evaluate the durability of the treatment and the potential for late complications.
There are also some potential risks associated with Prostate artery embolization. The most common complication is a temporary worsening of benign prostatic hyperplasia symptoms, which can occur in the days following the procedure. This is typically due to swelling of the prostate gland as a result of the embolization, and symptoms typically improve within a few days. Other potential complications include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding organs.
Patients who undergo Prostate artery embolization for benign prostatic hyperplasia typically experience rapid relief of symptoms, with many reporting significant improvement within a few days. Most patients are able to return to their normal activities within a week or two of the procedure. However, it is important to note that Prostate artery embolization is not a permanent cure for benign prostatic hyperplasia, and some patients may require additional treatment in the future.
In summary, prostate artery embolization is a minimally invasive procedure that is used to treat benign prostatic hyperplasia by reducing blood flow to the prostate gland, causing it to shrink in size and improve urinary symptoms. Prostate artery embolization has emerged as an alternative to traditional surgical treatments for benign prostatic hyperplasia, offering several advantages, including a lower risk of complications and a shorter recovery time. However, not all men with benign prostatic hyperplasia are suitable candidates for Prostate artery embolization, and more research is needed to evaluate the long-term effectiveness and safety of the procedure. Men with benign prostatic hyperplasia who are considering treatment should discuss all of their options with their healthcare provider to determine the best course of action for their individual situation.
Side Effects of a Large Prostate
- Inability to urinate
- Inability to fully empty your bladder
- Dribbling after urination
- Incontinence
- Pain with urination
- Straining with urination
- Delayed start when urinating
- Weak or slow urine stream
- Frequent urges to urinate at night (2 or more times)
The prostate gland is a small, walnut-sized organ that is located just below the bladder in men. It is an important part of the male reproductive system and plays a crucial role in the production of semen. As men age, the prostate gland can become enlarged, which can lead to a variety of uncomfortable symptoms and potential health risks.
An enlarged prostate, also known as benign prostatic hyperplasia, is a common condition that affects many men as they age. Benign prostatic hyperplasia occurs when the cells of the prostate gland begin to multiply, leading to an increase in the size of the gland. As the prostate gland grows, it can press against the urethra, the tube that carries urine from the bladder out of the body, and cause a variety of symptoms.
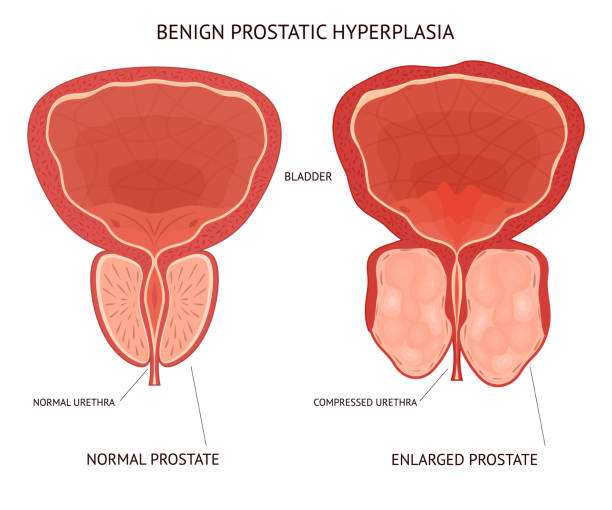
One of the most common symptoms of an enlarged prostate is difficulty urinating. As the prostate gland presses against the urethra, it can make it difficult for urine to pass through, leading to a weak or interrupted urine stream, the need to strain to start urinating, and the feeling of not being able to completely empty the bladder. This can be very uncomfortable and can lead to frequent trips to the bathroom, especially at night.
Another common symptom of an enlarged prostate is a frequent need to urinate. The pressure on the bladder from an enlarged prostate can cause the bladder to become more sensitive, leading to the feeling of needing to urinate more often, even if the bladder is not full. This can be very disruptive to daily life and can make it difficult to get a good night’s sleep.
In addition to these urinary symptoms, an enlarged prostate can also cause other health problems. For example, if the bladder is not completely emptied during urination, it can increase the risk of urinary tract infections. An enlarged prostate can also lead to bladder stones or even kidney damage if left untreated.
Fortunately, there are many treatments available for an enlarged prostate, ranging from lifestyle changes to medications to surgical procedures. Lifestyle changes such as reducing caffeine and alcohol intake and avoiding fluids before bedtime can help reduce the frequency of urination. Medications such as alpha-blockers and 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can help relax the muscles of the prostate and reduce its size. And in some cases, surgical procedures such as transurethral resection of the prostate or laser surgery may be necessary to remove excess prostate tissue.
While these treatments can be very effective, they can also have side effects of their own. For example, alpha-blockers can cause dizziness or low blood pressure, especially when standing up quickly. 5-alpha reductase inhibitors can cause sexual side effects such as decreased libido or erectile dysfunction. And surgical procedures can carry risks such as bleeding or infection.
In addition to these side effects, there are also potential long-term health risks associated with treatments for an enlarged prostate. For example, some studies have suggested that the use of 5-alpha reductase inhibitors may increase the risk of high-grade prostate cancer, although this risk appears to be small. And while surgical procedures are generally safe, they can carry a small risk of serious complications such as urinary incontinence or impotence.
Overall, an enlarged prostate can be a very uncomfortable and disruptive condition that can have a significant impact on a man’s quality of life. While there are many treatments available, it is important to weigh the potential benefits and risks of each treatment option carefully. Men with an enlarged prostate should work closely with their healthcare providers to determine the best course of treatment for their individual needs and preferences. By working together, they can develop a personalized treatment plan that balances symptom relief with minimizing potential side effects and long-term health risks.
Recovery Time
The recovery time after Prostate artery embolization varies depending on the individual patient and the extent of the procedure. In general, most patients are able to go home the same day as the procedure or the next day. However, it is important to note that patients will need to arrange for transportation home, as they will not be able to drive themselves.
Patients may experience some discomfort or pain after Prostate artery embolization, but this can usually be managed with over-the-counter pain medication. It is normal to experience some swelling or bruising around the groin area where the catheter was inserted, but this should subside within a few days.
In the weeks following Prostate artery embolization, patients may experience some urinary symptoms such as increased frequency, urgency, or difficulty urinating. However, these symptoms typically improve over time as the prostate gland shrinks. Patients should drink plenty of fluids and avoid caffeine and alcohol to help manage these symptoms.
Most patients are able to return to work and resume normal activities within a week or two after Prostate artery embolization. However, it is important to avoid strenuous exercise or heavy lifting for at least a week after the procedure to allow the groin area to heal.
It is important for patients to follow their doctor’s instructions carefully during the recovery period after Prostate artery embolization. This may include taking medications to manage pain or urinary symptoms, as well as scheduling follow-up appointments to monitor the progress of the procedure.
In rare cases, patients may experience complications after Prostate artery embolization, such as bleeding, infection, or damage to surrounding tissues. Patients should contact their doctor immediately if they experience severe pain, fever, or any other unusual symptoms.
Overall, Prostate artery embolization is a promising treatment option for men with benign prostatic hyperplasia. While the recovery time after Prostate artery embolization varies depending on the individual patient, most patients are able to return to normal activities within a week or two. By following their doctor’s instructions and monitoring their symptoms carefully, patients can maximize the benefits of Prostate artery embolization and minimize the risk of complications.
Who is the best candidate for Prostate artery embolization
When it comes to identifying the best candidate for prostate artery embolization, there are several factors to consider. First and foremost, the patient must have an enlarged prostate gland that is causing bothersome symptoms. Additionally, the patient should be in good overall health and not have any underlying medical conditions that would make them a poor candidate for the procedure. Other factors that may be taken into account include the size and shape of the prostate gland, as well as the severity of the patient’s symptoms.
Another factor to consider when identifying the best candidate for prostate artery embolization is the patient’s age. While the procedure can be performed on men of any age, it is typically recommended for men who are in their 50s or 60s. This is because the procedure is more effective in men with larger prostate glands, which tend to occur in older men.
In addition to age, the severity of the patient’s symptoms may also play a role in determining whether or not they are a good candidate for prostate artery embolization. Men with mild to moderate symptoms may benefit from the procedure, as it can help to reduce the size of the prostate gland and improve urinary function. However, men with severe symptoms may require more aggressive treatment options, such as surgery or medication.
Where to go for Prostate Artery Embolization?
The first step in finding a provider for prostate artery embolization is to talk to your healthcare provider. They can help you understand if this treatment option is right for you and refer you to a specialist who performs the procedure. Your healthcare provider may have a specific provider in mind or recommend a list of providers in your area for you to choose from.
Another option is to research providers who offer prostate artery embolization online. Many medical centers and hospitals have websites that provide information on the services they offer and the physicians who perform them. You can also search for providers on medical directory websites, such as Healthgrades or Vitals, which provide information on physician credentials, patient reviews, and ratings.
When choosing a provider for prostate artery embolization, it is important to consider their experience and expertise in performing the procedure. Look for providers who specialize in interventional radiology or have extensive experience performing prostate artery embolization. You can usually find this information on the provider’s website or by calling their office directly.
In addition to experience, it is important to consider the provider’s location and accessibility. Look for a provider who is conveniently located and easily accessible from your home or workplace. You may also want to consider the provider’s availability and scheduling flexibility to ensure that you can schedule the procedure at a time that works best for you.
Another important factor to consider when choosing a provider for prostate artery embolization is their reputation and patient satisfaction. Look for providers who have a good reputation in the medical community and positive patient reviews. You can usually find patient reviews on the provider’s website or on third-party review sites.
Finally, it is important to consider the cost of prostate artery embolization and whether or not your insurance will cover the procedure. Some providers may offer financial assistance or have payment plans available to help make the procedure more affordable. It is important to check with your insurance provider to understand the extent of your coverage and any out-of-pocket costs you may be responsible for.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is prostate artery embolization?
Answer: Prostate artery embolization (PAE) is a minimally invasive procedure used to treat symptoms of an enlarged prostate gland.
-
Who can perform prostate artery embolization?
Answer: Prostate artery embolization is typically performed by interventional radiologists who have extensive experience in performing the procedure.
-
How can I find a provider for prostate artery embolization?
Answer: You can find a provider for prostate artery embolization by talking to your healthcare provider, researching providers online, or contacting medical centers and hospitals in your area.
-
What should I consider when choosing a provider for prostate artery embolization?
Answer: When choosing a provider for prostate artery embolization, you should consider their experience, expertise, location, accessibility, reputation, patient satisfaction, and cost.
-
What types of providers offer prostate artery embolization?
Answer: Prostate artery embolization is typically offered by interventional radiologists, but some urologists may also offer the procedure.
-
Is prostate artery embolization covered by insurance?
Answer: Prostate artery embolization is usually covered by insurance, but it is important to check with your insurance provider to understand the extent of your coverage and any out-of-pocket costs.
-
What is the success rate of prostate artery embolization?
Answer: Prostate artery embolization has a high success rate in reducing symptoms of an enlarged prostate, with studies reporting a success rate of over 90%.
-
What are the risks of prostate artery embolization?
Answer: The risks of prostate artery embolization are generally low, but may include bleeding, infection, and damage to surrounding tissue.
-
How long does a prostate artery embolization procedure take?
Answer: A prostate artery embolization procedure typically takes between 1-2 hours to complete.
-
How long is the recovery time after a prostate artery embolization procedure?
Answer: Recovery time after a prostate artery embolization procedure is generally short, with most patients able to return to normal activities within a few days. However, it may take up to several weeks for symptoms to improve.

