Managing Your Life with Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. It occurs when the body is unable to regulate blood sugar levels properly, leading to high blood sugar levels over time. While diabetes cannot be cured, it can be managed effectively with the right tools and techniques. In this essay, we will explore diabetes care and some strategies for managing your life with diabetes.

There are three types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes– Your body is not able to produce insulin.
- Type 2 Diabetes– Also known as the most common type of diabetes, your body is unable to make or use insulin well.
- Gestational Diabetes (GD) – Otherwise known as Pregnancy Diabetes, this type of diabetes usually goes away after the birth of the baby. However, even if it does go away, women who have had GD have a higher chance of developing diabetes later in life.
Understanding Diabetes
Before we delve into specific health problems and strategies for managing diabetes, it is essential to understand the condition itself. There are two main types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is an autoimmune disorder that occurs when the immune system attacks and destroys the cells in the pancreas that produce insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, so without it, blood sugar levels can rise dangerously high. Type 1 diabetes usually develops in childhood or adolescence and requires lifelong insulin therapy.
Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, is a metabolic disorder that occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough insulin to regulate blood sugar levels effectively. Type 2 diabetes is usually associated with lifestyle factors such as obesity, lack of exercise, and poor diet, although genetics also play a role. Type 2 diabetes can often be managed with lifestyle changes and medication, although some people may also require insulin therapy.
Regardless of the type of diabetes, the goal of treatment is to keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range to prevent complications from diabetes medications such as heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, and nerve damage. Achieving this goal requires a combination of medication, diet, exercise, and monitoring.
Medication
Medication is an essential part of diabetes management, and there are several types of medication that are commonly used. For type 1 diabetes, insulin therapy is the mainstay of treatment. Insulin can be delivered via injection or insulin pump and is typically given several times a day.
For type 2 diabetes, medication may include oral medications that help lower blood sugar levels, such as metformin or sulfonylureas. In some cases, injectable medications such as GLP-1 agonists or insulin may also be necessary.
It is important to work closely with your healthcare team to find the right food and medication regimen for you and to monitor your blood sugar levels regularly to ensure that your medication is working effectively.
Diet

Diet is another crucial aspect of managing diabetes. A healthy diet can help keep blood sugar levels within a healthy range, promote weight loss if necessary, control it, and reduce the risk of complications.
For the health of people with diabetes, it is important to focus on eating a balanced diet that includes plenty of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean protein, and healthy fats. Foods that are high in sugar, refined carbohydrates, and saturated or trans fats should be limited or avoided.
It is also important to pay attention to portion sizes and to spread out meals and snacks throughout the day to avoid spikes in blood sugar levels. Working with a registered dietitian who specializes in diabetes management can be helpful in developing a personalized meal plan.
Exercise

Exercise is another critical component of managing diabetes. Exercise helps lower blood sugar levels, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote weight loss.
For people with diabetes, it is important to aim for at least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise per week. This can include activities such as brisk walking, cycling, swimming, or dancing. Strength training exercises should also be incorporated at least twice a week.
It is essential to talk to your doctor and work with your healthcare team to develop an exercise plan that is safe and effective for you, especially if you have other health conditions or complications.
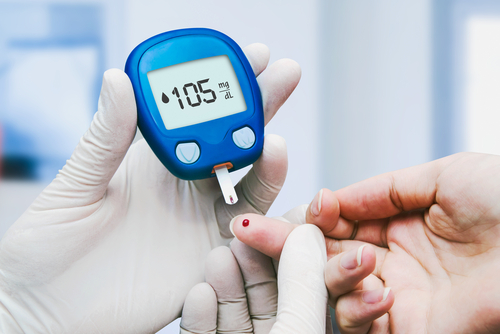
Monitoring
Monitoring blood sugar levels regularly is essential for managing diabetes effectively. This allows you to track how your medication, diet, and exercise are affecting your blood sugar levels and make adjustments as needed to manage diabetes well.
There are several ways to monitor blood sugar levels, including self-monitoring of blood glucose (SMBG) and continuous glucose monitoring (CGM). SMBG involves using a blood glucose meter to check your blood sugar levels at various times throughout the day, while CGM involves wearing a sensor that continuously measures your blood sugar levels and sends the data to your doctor via a receiver or smartphone app.
It is essential to work with your healthcare team to determine the best blood sugars monitoring strategy for you and to establish target blood sugar levels that are appropriate for your individual needs and goals.
Managing Diabetes on a Daily Basis
Managing diabetes can be challenging, but it is essential to make it a part of your daily and mental health and routine. Here are some tips for managing diabetes on a daily basis:
- Stick to a regular meal plan and eat meals and snacks at consistent times each day.
- Make physical activity a part of your daily routine, whether it’s taking a walk during your lunch break or joining a fitness class.
- Take your medication as prescribed and monitor your blood sugar levels regularly.
- Make sure to stay hydrated by drinking plenty of water throughout the day.
- Get enough restful sleep each night, as lack of sleep can affect blood sugar levels.
- Stay connected with your healthcare team and attend regular appointments to monitor your diabetes and manage any complications that may arise.
- Learn to manage stress effectively through relaxation techniques such as meditation or deep breathing.
- Take care of your feet by wearing comfortable, well-fitting shoes and checking them daily for any cuts or sores.
- Keep an emergency kit with you at all times that includes snacks, medication, and glucose tablets or gel in case of low blood sugar.
- Join a diabetes support group or online community to connect with others who are also managing diabetes and learn from their experiences.
Conclusion
Managing your life with diabetes requires a multi-faceted approach to health care that involves medication, diet, exercise, monitoring, and lifestyle adjustments. While it can be challenging, with the right tools and techniques, it is possible to live a healthy, fulfilling life with diabetes. By working closely with your healthcare team, developing a daily routine, and staying committed to your diabetes management plan, you can reduce your risk of complications and enjoy a high quality of life.
Did you know that people with Diabetes are also at high risk for developing Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)? The leading symptom is pain and cramping in the legs. Take our quiz to see if you may be symptomatic! Follow this link- https://go.myvascular.com/vascular-disease-survey-az.
Frequently Asked Questions
-
What is diabetes?
Answer: Diabetes is a chronic condition in which the body either does not produce enough insulin or does not properly use the insulin it produces, leading to high levels of sugar (glucose) in the blood.
-
What are the types of diabetes?
Answer: The two main types of diabetes are type 1 diabetes, which is an autoimmune disease that usually develops in childhood or adolescence, and type 2 diabetes, which is often associated with obesity and insulin resistance and typically develops in adulthood.
-
What are the symptoms of diabetes?
Answer: Common symptoms of diabetes include frequent urination, excessive thirst, unexplained weight loss, increased hunger, fatigue, blurred vision, and slow-healing sores or cuts.
-
What are the risk factors for developing diabetes?
Answer: Risk factors for developing type 2 diabetes include being overweight or obese, having a family history of diabetes, being physically inactive, and having high blood pressure or high cholesterol.
-
How is diabetes diagnosed?
Answer: Diabetes is typically diagnosed through a blood test that measures the level of glucose in the blood after fasting for several hours or after drinking a sugary drink.
-
How is diabetes treated?
Answer: Diabetes is typically managed through a combination of lifestyle changes, such as eating a healthy diet and getting regular exercise, and medication, such as insulin injections or oral medications that help regulate blood sugar levels.
-
What are the long-term complications of diabetes?
Answer: Diabetes can lead to a number of long-term complications, including nerve damage, kidney damage, eye damage, and an increased risk of heart disease and stroke.
-
How can diabetes be prevented?
Answer: Type 1 diabetes cannot be prevented, but type 2 diabetes can often be prevented or delayed through lifestyle changes such as maintaining a healthy weight, getting regular exercise, and eating a healthy diet.
-
What are some common myths about diabetes?
Answer: Common myths about diabetes include that it is caused by eating too much sugar, that people with diabetes can’t eat any carbohydrates, and that people with diabetes can’t participate in physical activity.
-
What resources are available for people with diabetes?
Answer: There are many resources available for people with diabetes, including support groups, online communities, and educational programs offered by healthcare providers and organizations such as the American Diabetes Association.
Did you know that people with Diabetes are also at high risk for developing Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)? The leading symptom is pain and cramping in the legs. Take our quiz to see if you may be symptomatic! Follow this link- https://go.myvascular.com/vascular-disease-survey-az.